- Topics similar to or like. Heliocentric orbit. Orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. Fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System.
- There was a recent news item about Star Trek's Kate Mulgrew in a geocentric movie.The geocentric model states that the Sun and the planets move around the Earth instead of the heliocentric model.
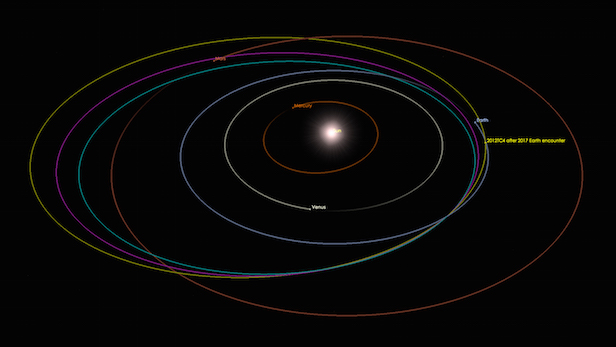
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun.[1]
34 relations: Anthropomorphism, Asteroid, Barycenter, Bi-elliptic transfer, Comet, Delta-v, Doppler spectroscopy, Earth's orbit, Exoplanet, Gas giant, Geocentric orbit, Greek language, Greek mythology, Heliocentrism, Helios, Hohmann transfer orbit, Jupiter, List of artificial objects in heliocentric orbit, List of orbits, Low-energy transfer, Luna 1, Mars Orbiter Mission, MAVEN, Orbit, Orbital maneuver, Orbital mechanics, Planet, Random House, Solar System, Space debris, Space probe, Spacecraft, Sun, Trajectory.
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun.All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun itself are in such orbits, as are many artificial probes and pieces of debris.The moons of planets in the Solar System, by contrast, are not in. In this orbit the spacecraft slowly drifts away from the Earth and is at a distance of 0.5 Astronomical Unit (AU) (worst case) at the end of four years. Another advantage of this orbit is that it has a very-low disturbing torque on the spacecraft, which leads to a very stable pointing attitude.
Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Anthropomorphism · See more »
Asteroid
Asteroids are minor planets, especially those of the inner Solar System.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Asteroid · See more »
Barycenter
The barycenter (or barycentre; from the Ancient Greek βαρύς heavy + κέντρον centre) is the center of mass of two or more bodies that are orbiting each other, which is the point around which they both orbit.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Barycenter · See more »
Bi-elliptic transfer
In astronautics and aerospace engineering, the bi-elliptic transfer is an orbital maneuver that moves a spacecraft from one orbit to another and may, in certain situations, require less delta-v than a Hohmann transfer maneuver.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Bi-elliptic transfer · See more »
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process called outgassing.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Comet · See more »
Delta-v
Delta-v (literally 'change in velocity'), symbolised as ∆v and pronounced delta-vee, as used in spacecraft flight dynamics, is a measure of the impulse that is needed to perform a maneuver such as launch from, or landing on a planet or moon, or in-space orbital maneuver.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Delta-v · See more »
Doppler spectroscopy
Doppler spectroscopy (also known as the radial-velocity method, or colloquially, the wobble method) is an indirect method for finding extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs from radial-velocity measurements via observation of Doppler shifts in the spectrum of the planet's parent star. Candy crush game free download mac.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Doppler spectroscopy · See more »
Earth's orbit
Earth's orbit is the trajectory along which Earth travels around the Sun.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Earth's orbit · See more »
Exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside our solar system.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Exoplanet · See more »
Gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Gas giant · See more »
Geocentric orbit
A geocentric orbit or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Planet Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites.
Heliocentric Orbit Satellite
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Geocentric orbit · See more »
Greek language
Greek (Modern Greek: ελληνικά, elliniká, 'Greek', ελληνική γλώσσα, ellinikí glóssa, 'Greek language') is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece and other parts of the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Greek language · See more »
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and teachings that belong to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices.

New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Greek mythology · See more »
Heliocentric Orbit Vs Geocentric
Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the Solar System.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Heliocentrism · See more »
Helios
Helios (Ἥλιος Hēlios; Latinized as Helius; Ἠέλιος in Homeric Greek) is the god and personification of the Sun in Greek mythology.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Helios · See more »
Hohmann transfer orbit
In orbital mechanics, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit used to transfer between two circular orbits of different radii in the same plane.
Free download kundli software for mac os x. New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Hohmann transfer orbit · See more »
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Jupiter · See more »
List of artificial objects in heliocentric orbit
Below is a list of artificial objects in heliocentric orbit.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and List of artificial objects in heliocentric orbit · See more »
List of orbits
The following is a list of types of orbits.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and List of orbits · See more »
Low-energy transfer
A low-energy transfer, or low-energy trajectory, is a route in space that allows spacecraft to change orbits using very little fuel.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Low-energy transfer · See more »
Luna 1
Luna 1, also known as Mechta (Мечта, lit.: Dream), E-1 No.4 and First Lunar Rover, was the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Earth's Moon, and the first spacecraft to be placed in heliocentric orbit.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Luna 1 · See more »
Mars Orbiter Mission
The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), also called Mangalyaan ('Mars-craft', from मंगल mangala, 'Mars' and यान yāna, 'craft, vehicle'), is a space probe orbiting Mars since 24 September 2014.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Mars Orbiter Mission · See more »
MAVEN
Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission (MAVEN) is a space probe developed by NASA to study the Martian atmosphere while orbiting Mars.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and MAVEN · See more »
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved trajectory of an object, such as the trajectory of a planet around a star or a natural satellite around a planet.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Orbit · See more »
Orbital maneuver
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Orbital maneuver · See more »
Orbital mechanics

Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Orbital mechanics · See more »
Planet
A planet is an astronomical body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Planet · See more »
Random House
Random House is an American book publisher and the largest general-interest paperback publisher in the world.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Random House · See more »
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Solar System · See more »
Space debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space waste, space trash, space litter or space garbage) is a term for the mass of defunct, artificially created objects in space, most notably in Earth orbit, such as old satellites and spent rocket stages.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Space debris · See more »
Space probe
A space probe is a robotic spacecraft that does not orbit the Earth, but, instead, explores further into outer space.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Space probe · See more »
Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Spacecraft · See more »

Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Sun · See more »
Trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that a massive object in motion follows through space as a function of time.
New!!: Heliocentric orbit and Trajectory · See more »
Redirects here:
Circumsolar orbit, Circumsolar orbits, Heliocentric orbits, Mars transfer orbit, Solar orbit, Trans Mars Injection, Trans-Mars Injection, Trans-Mars injection.
References

[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heliocentric_orbit
