In my developer toolbox post, I’ve covered that I prefer to use to MAMP for local development. For the most part, the default settings (or some variation thereof) work just fine; however, if you end up needing to do some work on a secure site, then you’ll need enable SSL in MAMP.
MAMP (Mac, Apache, MySQL, PHP) is a free and premium local server environment that can be installed on the macOS and Windows operating systems. The free version of MAMP provides all the tools you will need to run WordPress on your PC for testing and development purposes. Installing MAMP. Download MAMP and run the installation exe. Warning, a reboot is required at the end. Choose language. Untick those pre-selected check boxes. MAMP PRO is for the web devs & MAMP Viewer is for alternative platform (iOS) viewing of your website. MAMP (Mac, Apache, MySQL, PHP) is a free and premium local server environment that can be installed on the macOS and Windows operating systems. The free version of MAMP provides all the tools you will need to run WordPress on your PC for testing and development purposes. MAMP stands for M acintosh, A pache, M ySQL, and P HP. This reflects the fact that MAMP was originally developed for use on Macs, but it now runs on Windows and Linux too and is the easiest way to run WordPress locally. MAMP is free software that lets you run Apache and PHP on your computer, both of which you need to run WordPress locally.
On production-level servers, you’ll need to have purchased an SSL certificate; however, MAMP makes it trivially easy to setup a certificate in your development environment.
Enable SSL in MAMP
The only caveat to setting up SSL on your development machine is that you have to define a local server other than localhost (but this is easy to do).
Other than that, it’s just a few simple steps.
1. Load MAMP
First, load MAMP and make sure that you’re on the homescreen. If you’re more comfortable with MAMP, then it doesn’t really matter which screen you start on – this step ensures that we’re all on the same page.

2. Define a New Host
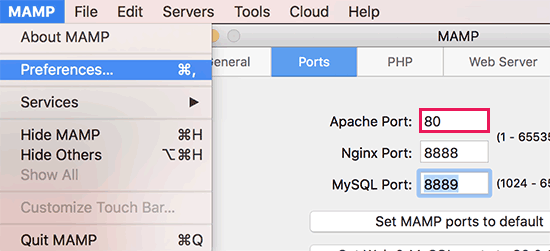
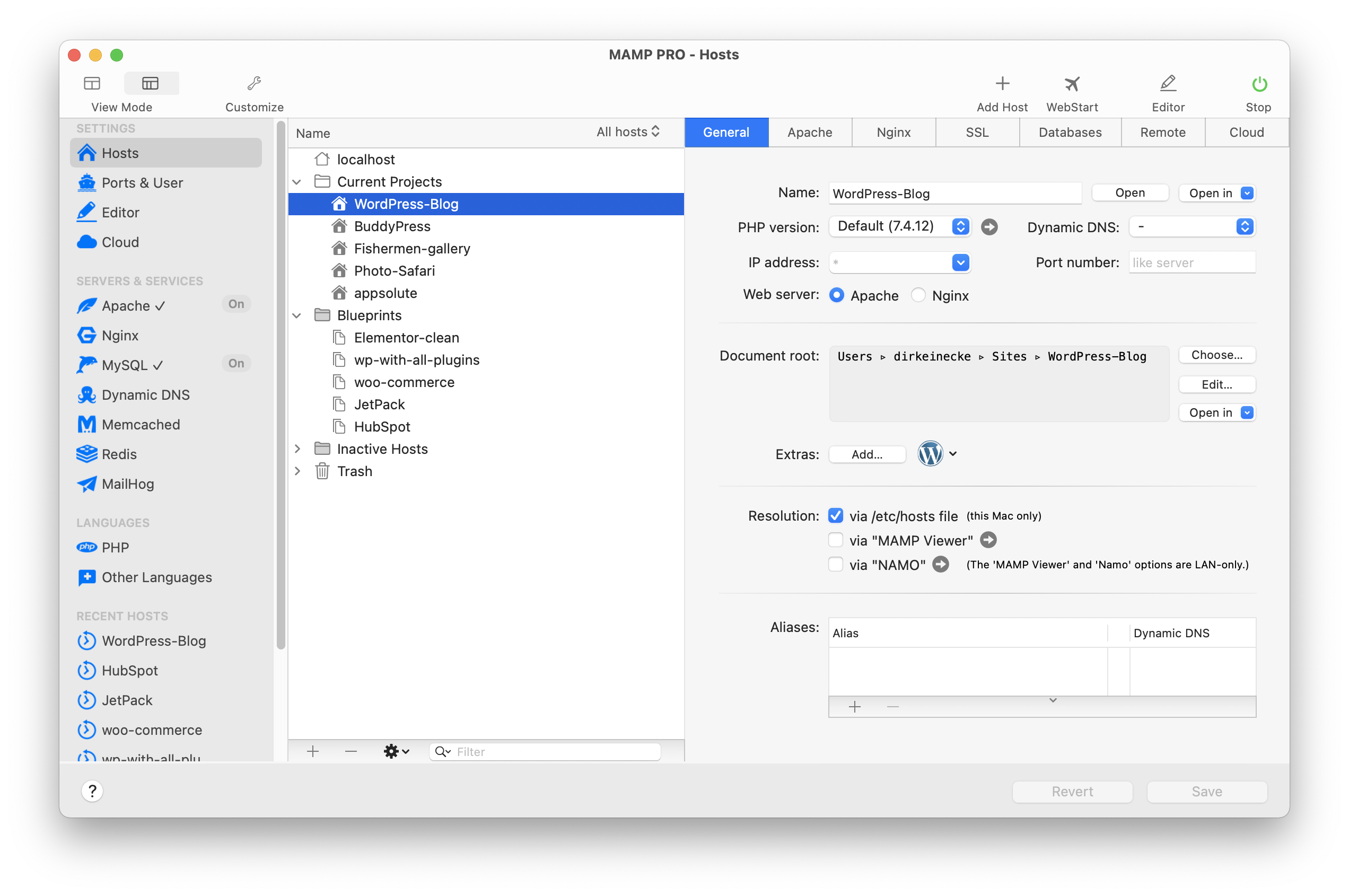
Click on the “Hosts” tab to view the list of the hosts you’ve configured. Some of you will only have ‘localhost’, others of you will have more.
Regardless, click on the ‘+’ button right below the list of hosts to add a new host. This will automatically insert a new line item into the list of hosts and will display a set of fields for you to populate:
Make sure that you click on the ‘SSL’ check box:
Then select the directory out of which your site, application, or files will be served:
3. Generate an SSL Certificate
After that, click on the ‘SSL’ tab. Initially, you should see two fields each of which have an exclamation point beside them:
Next, click on the ‘Create Self-Signed Certificate’ button and a new dialog will appear prompting you to populate it with certain information: Avg cleaner mac free download.
Fill out this information. Feel free to be as accurate – or inaccurate) – as you want as this information is kept on your local machine:
Finally, click on ‘Generate’ and you’ll be asked where to save the certificate file. Feel free to choose any location. I’m a fan of keeping the certificate file in the same location of the project just to keep things organized.
4. Done!
Once you’ve generated the certificate, MAMP will automatically populate the fields with the locations of both the certificate file and the key file.
Finally, restart your server.
Once the server has restarted, you can navigate to your secure site using the host you defined earlier in this process. In my case, it would be https://examplehost.net. Remember to prefix the location with https; otherwise, it won’t load.
And that’s how you enable SSL in MAMP. Easy enough, right?
Topics
- Other WordPress Development Tools
Why set up a development environment? Why set up a development environment?
When developing themes, it is best to do it in an environment identical to the production server which will eventually host your WordPress installation. Your development environment can either be local or remote. Configuring a local environment to work on your WordPress theme is beneficial for several reasons:
Mamp Server
- You can build your theme locally without relying on a remote server. This speeds up your development process and allows you to see changes instantly in your browser.
- You do not need an Internet connection to build your theme.
- You can test your theme from a variety of perspectives. This is important, especially if you plan on releasing your theme to a larger audience and want to ensure maximum compatibility.
Your WordPress local development environment Your WordPress local development environment
For developing WordPress themes, you need to set up a development environment suited to WordPress. To get started, you will need a local server stack and a text editor. There are a number of options, including:
Local Server Stack
- A local server stack, such as LAMP (Linux Apache MySQL/MariaDB PHP) or WAMP (Windows Apache MySQL/MariaDB PHP) is a server (much like the server that runs on your web server), which you will configure on your local machine. You can install pre-bundled programs that contain all of these, like MAMP (for Mac), or XAMPP (Mac or Windows) to quickly setup your environment.

Virtualized Environment
- A virtualized such created with Vagrant and VirtualBox allows you to create easily reproducible development environments. Varying Vagrant Vagrants (VVV) is a popular Vagrant option which creates a WordPress development environment.
Text Editor
In addition to a local server environment, you also need a text editor to write your code. Your choice of text editor is personal, but remember that a good text editor can speed up your development process. Your text editor can be everything from a basic tool for writing code to a fully integrated development environment (IDE) with tools for debugging and testing. It’s worth doing research, and some even include support for WordPress development. Popular choices are Atom, Sublime Text, and PhpStorm.
You can find a list of tutorials for setting up development environments at the bottom of the page.
Supporting older versions of WordPress Supporting older versions of WordPress
It’s standard practice for WordPress themes to support at least two versions back to ensure a minimum of backward compatibility. For example, if the current version of WordPress is at 4.6, then you should also make sure that your theme works well in versions 4.5 and 4.4 as well.
You can refer to the WordPress Releases page to access older versions of WordPress. Then you can download and install older WordPress versions, creating multiple development sites, each running different WordPress versions for testing.
WP_DEBUG WP_DEBUG
Configuring debugging is an essential part of WordPress theme development. WordPress provides a number of constants to support your debugging efforts. These includes:
WP_DEBUG
The WP_DEBUG PHP constant is used to trigger the built-in “debug” mode on your WordPress installation. This allows you to view errors in your theme. To enable it:
1. Open your WordPress installation’s wp-config.php file
2. Change:
to
WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY and WP_DEBUG_LOG
WP_DEBUG_LOG and WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY are additional PHP constants which extend WP_DEBUG.
WP_DEBUG_LOG is used in conjunction with WP_DEBUG to log all error messages to a debug.log within your WordPress /wp-content/ directory. To enable this functionality set WP_DEBUG_LOG to true within your wp-config.php file.
WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY is used to control whether debug messages display within the HTML of your theme pages. To display error messages on the screen as they occur, configure this setting to ‘true’ within your wp-config.php file.
With the WP_DEBUG and WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY enabled, error messages will display at the top of your site pages.
Note: Errors will display in the frontend and admin areas of your site. These debug tools are meant for local testing and staging installs, not for live sites.
Other WordPress Development Tools Other WordPress Development Tools
In addition to WP_DEBUG, the following plugins and unit test data sets are an important part of your development toolset and help you develop better WordPress themes.
Test DataTest Data
WordPress.org Theme Unit Test Data
WordPress.org Theme Unit Test Data is an XML file containing dummy test data that you can upload to test how themes perform with different types and layouts of content.
WordPress.com Theme Unit Test Data
WordPress.com Theme Unit Test Data is dummy test data that you can upload to a WordPress installation to test your theme, including WordPress.com-specific features.
PluginsPlugins
Studio one 4 download mac. Debug Bar(WordPress plugin)
Debug Bar adds an admin bar to your WordPress admin providing a central location for debugging.
Query Monitor(WordPress plugin)
Query Monitor allows debugging of database queries, API request and AJAX called used to generate theme pages and theme functionality.
Log Deprecated Notices(WordPress plugin)
Log Deprecated Notices logs incorrect function usage and the use of deprecated files and functions in your WordPress theme.
Mamp Wordpress Local
Monster Widgets(WordPress plugin)
Monster Widget consolidates the core WordPress widgets into a single widget allowing you to test widgets styling and functionality in your theme.
Developer (WordPress plugin)
Developer helps optimize your development environment by allowing easy installation of tools and plugins that help in troubleshooting and ensuring code quality.
Theme-Check (WordPress plugin)
Theme-Checktests your theme for compliance with the latest WordPress standards and practices.
Mamp Wordpress Windows
WordPress Theme Review Guidelines WordPress Theme Review Guidelines
Mamp Wordpress Windows 10
In addition to the above development tools, it’s a good idea to stay up to date on the WordPress.org Theme Review Team’s Guidelines for theme submission and guidance on meeting WordPress Coding Standards. These guidelines are the “gold standard” for quality theme development and are useful, even if you don’t plan on releasing a theme on WordPress.org.
Further Resources Further Resources
- Developing WordPress Locally With MAMP (Mac, MAMP)
- How to Setup a WordPress Development Environment for Windows (Windows, XAMPP)
- WordPress Theme Review VVV: A Quick Vagrant Setup for Testing Themes (Cross-platform, Vagrant)
- Setting up your Development Environment (WordPress.com VIP)
- wptest.io – an exhaustive set of WordPress test data derived from WordPress’ Theme Unit Test
